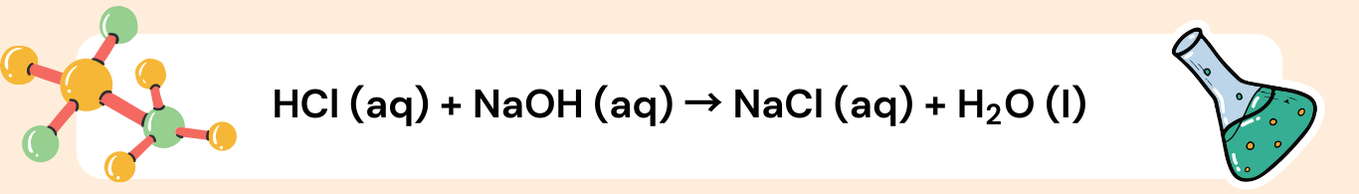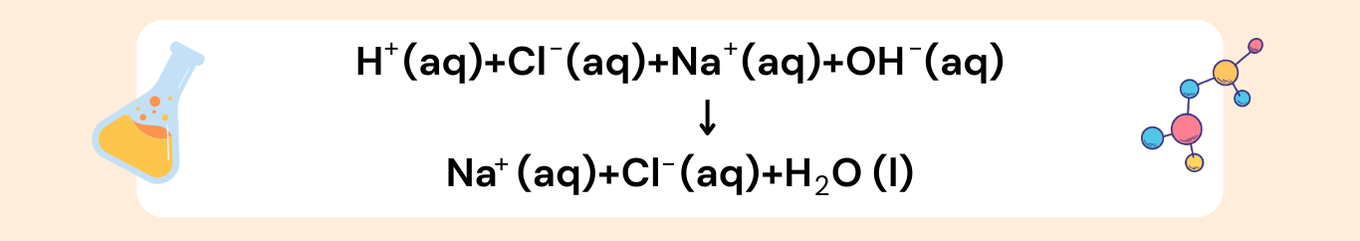- Oct 2, 2024 - 7 min read
How to Balance Ionic Equations: A Guide for O-Level Chemistry Student

In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the steps of writing and balancing ionic equations, and why this is an important concept in your GCE Chemistry syllabus. If you’re preparing for your O-Level exams, or you need help from a chemistry tutor, this guide is for you.

1. What are Ionic Equations?
For example, instead of writing a full balanced chemical equation for a reaction, ionic equations show the ions that actually participate in the chemical change. This makes it easier to understand which substances are reacting and which are simply “spectators” in the reaction.

2. Writing Ionic Equations
a) Write the full balanced chemical equation.
Make sure the equation follows the law of conservation of mass. This is crucial for both traditional chemical equations and ionic equations.b) Separate aqueous compounds into their respective ions.
Only compounds that are soluble in water (aqueous) should be split into ions. For instance, NaCl(aq) becomes Na⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq), while solids, liquids, and gases remain unchanged.
c) Identify and cancel out spectator ions.
Spectator ions are ions that do not change during the course of the reaction. They appear on both sides of the equation and can be canceled out, leaving you with the net ionic equation.

3. The Importance of Balancing Ionic Equations in O-Level Chemistry
|
|

4. Steps to Balancing Ionic Equations
- Write the skeletal equation for the reaction, including only the ions and molecules directly involved in the chemical change.
- Balance the atoms in the equation, starting with atoms that appear only once on each side. Use coefficients, not subscripts, to balance the number of atoms.
- Balance the charge. This is a key difference between balancing traditional chemical equations and ionic equations. You need to ensure that the total charge on both sides of the equation is the same.
- Check your work by making sure both the number of atoms and the charges are balanced.
Example: Balancing a Simple Ionic Equation
Separate into ions:
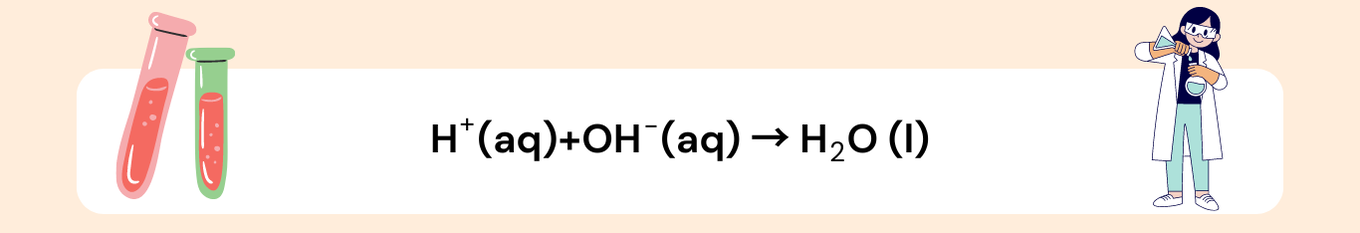
Cancel out spectator ions:
- The Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions appear on both sides, so they are spectator ions.
- The net ionic equation is:

5. Tips for Success in GCE Chemistry
a) Practice regularly: Like balancing chemical equations, mastering ionic equations requires consistent practice. Try working on different types of reactions, including precipitation, neutralization, and redox reactions.
b) Get help when needed: If you’re finding it hard to keep up with these concepts, don’t hesitate to seek help. Many students find chemistry tuition useful in breaking down difficult topics like writing ionic equations.
c) Use resources: Whether you’re studying independently or with the help of a chemistry tutor, make sure to use past GCE Chemistry papers and mock exams to sharpen your skills.
Conclusion
Understanding how to balance ionic equations is a crucial part of O-Level Chemistry, and it’s a skill that will help you in both exams and practical chemistry.
If you need extra support, enrolling in chemistry tuition or consulting with a chemistry tutor can give you the confidence you need to succeed. Keep practicing, and soon balancing equations will feel like second nature.